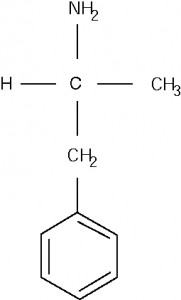
Amphetamines are psychomotor stimulants. They lead to the release of noradrenalin and dopamine, which are excitatory neurotransmitters. The many ways of consuming amphetamines are by injection, sniffing, snorting, or swallowing. They induce the feelings of strength, power, self-assertion, energy, heightened motivation, and focus. Dopamine release causes a prolonged sense of euphoria which is followed by fatigue and depression.
Amphetamine is related to ephedrine structurally. Ephedrine is a stimulant that is naturally found in the genus Ephedra. Amphetamine is also structurally similar to adrenaline, which is the ‘fight or flight’ hormone. Amphetamine was first artificially synthesized in 1887 in Germany by Edeleano. But it was only in the 1920s that its properties as a psychostimulant were recognized. Ephedra was found abundantly in China and the pharmaceutical companies were worried if the supply of the plant would be exhausted. Synthetic amphetamine was a simple and easy to manufacture substitute. Smith, Kline, and French brought out the Benzedrine Inhaler in 1932. This inhaler contained amphetamine which has the property of dilating the bronchial sacs, offering relief to people suffering from breathing problems.
Amphetamine sulphate was heavily prescribed for people suffering from hay fever, asthma, and even cold, and it was soon available as a pill. It was prescribed for epilepsy, depression, Parkinson’s disease, night-blindness, travel-sickness, obesity, hyperactive disorders of children, impotence, narcolepsy, and apathy in old age. During the Second World War soldiers consumed it without reserve. Even Hitler was known to receive daily injections of methamphetamine, which is derived from amphetamine. Some of the effects of methamphetamine usage are alertness, wakefulness, talkativeness, aggression, increased physical activity, increased initiative, higher self-confidence, and extreme elation. The negative effects of methamphetamine usage are depression, inertia, fatigue, psychosis, paranoia, and severe craving. It is also known to lead to brain damage;up to 11% loss of tissue in the brains of addicts has been recorded.
Tags: Amphetamines